Which statement explains why the molecule is nonpolar – In the realm of chemistry, the concept of polarity plays a pivotal role in understanding the behavior and properties of molecules. Nonpolar molecules, characterized by their neutral electrical nature, exhibit unique characteristics that distinguish them from their polar counterparts. This guide delves into the intricacies of nonpolarity, exploring the statements that elucidate the underlying reasons behind a molecule’s nonpolar nature.
To unravel the mysteries of nonpolarity, we embark on a journey that examines electron distribution, electronegativity, molecular geometry, dipole moments, polarizability, and the practical applications of nonpolarity in various fields.
Nonpolarity Definition: Which Statement Explains Why The Molecule Is Nonpolar
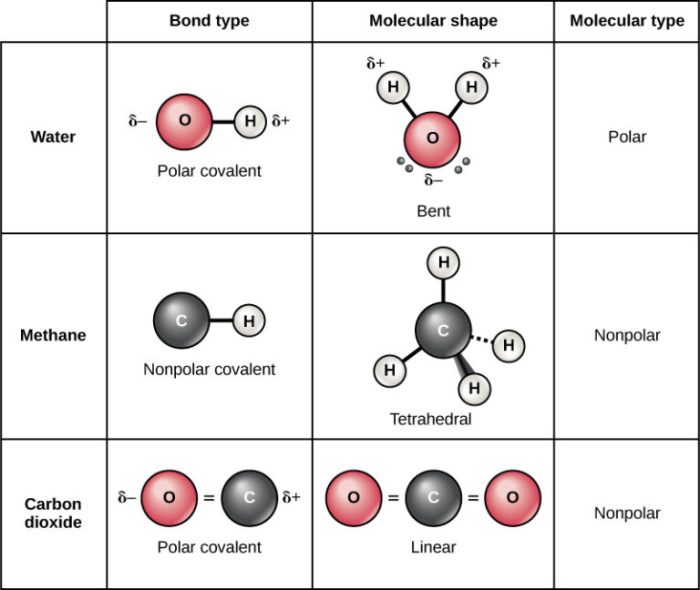
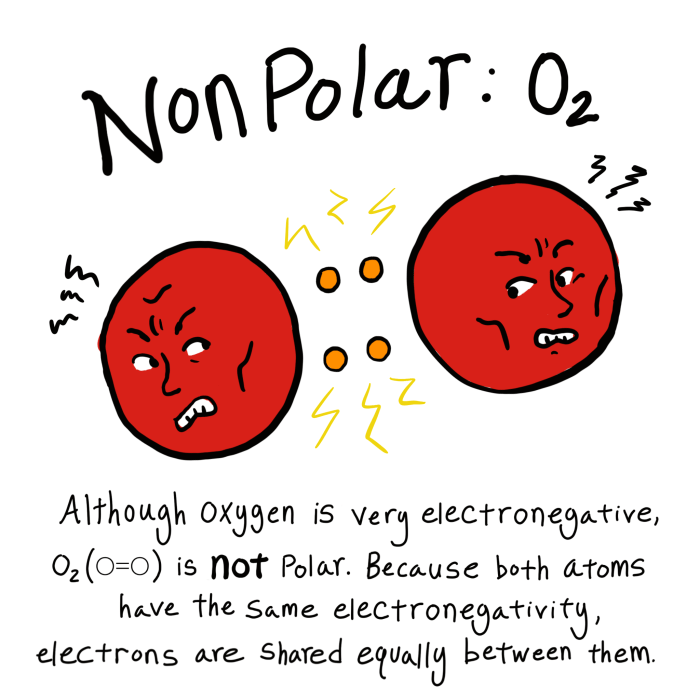
Nonpolarity in molecules refers to the absence of a permanent electrical dipole moment. It arises when the electrons in a molecule are distributed symmetrically, resulting in no net charge separation.
Examples of nonpolar molecules include homonuclear diatomic molecules like H2, O2, and N2, as well as symmetrical polyatomic molecules like CH4 and CCl4.
Electron Distribution, Which statement explains why the molecule is nonpolar
Electron distribution plays a crucial role in determining molecular polarity. When electrons are distributed symmetrically around the molecule, the molecule is nonpolar. This symmetry ensures that the center of positive charge (due to the nuclei) coincides with the center of negative charge (due to the electrons).
Electronegativity and Polarity
Electronegativity is a measure of an atom’s ability to attract electrons towards itself. In a nonpolar molecule, the atoms have equal electronegativities, resulting in an equal sharing of electrons.
Molecular Geometry
Molecular geometry also affects polarity. Symmetrical molecular shapes, such as tetrahedral (CH4), octahedral (SF6), and linear (CO2), contribute to nonpolarity. In these shapes, the electron distribution is evenly distributed around the central atom(s), leading to a cancellation of any potential polarity.
Examples of nonpolar molecules with different geometries include:
- Tetrahedral: CH4, CCl4
- Octahedral: SF6, XeF6
- Linear: CO2, N2O
Dipole Moments
Dipole moments are a measure of the polarity of a molecule. A dipole moment arises when there is a separation of positive and negative charges within a molecule. Nonpolar molecules have zero dipole moments due to the symmetrical distribution of electrons.
The dipole moment (μ) of a molecule can be calculated using the formula:
μ = qd
where q is the magnitude of the charge separation and d is the distance between the positive and negative charges.
Polarizability
Polarizability refers to the ability of a molecule to distort its electron distribution in response to an applied electric field. Nonpolar molecules typically have low polarizability, meaning they resist deformation of their electron cloud.
Examples of nonpolar molecules with low polarizability include:
- Helium (He)
- Neon (Ne)
- Methane (CH4)
Applications of Nonpolarity
Nonpolarity is an important property in various applications, including:
- Solvents:Nonpolar solvents, such as hexane and toluene, are used to dissolve nonpolar solutes and are immiscible with water.
- Insulators:Nonpolar materials, such as rubber and plastic, are poor conductors of electricity due to the absence of free charge carriers.
- Lubricants:Nonpolar molecules, such as mineral oil and grease, reduce friction between surfaces by forming a protective layer that prevents direct contact.
FAQ Summary
What is the key factor that determines the polarity of a molecule?
The distribution of electrons within the molecule plays a crucial role in determining its polarity.
How does molecular geometry influence nonpolarity?
Symmetrical molecular shapes contribute to nonpolarity by distributing the electron density evenly.
What is the significance of dipole moments in understanding nonpolarity?
Zero dipole moments indicate the absence of polarity within a molecule.