Which term describes the molecule shown below? This question sets the stage for an enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. As we delve into the intricacies of this molecule, we will uncover its structure, properties, reactivity, applications, and more, providing a comprehensive understanding of its significance in the scientific realm.
The content of the second paragraph that provides descriptive and clear information about the topic
Chemical Structure
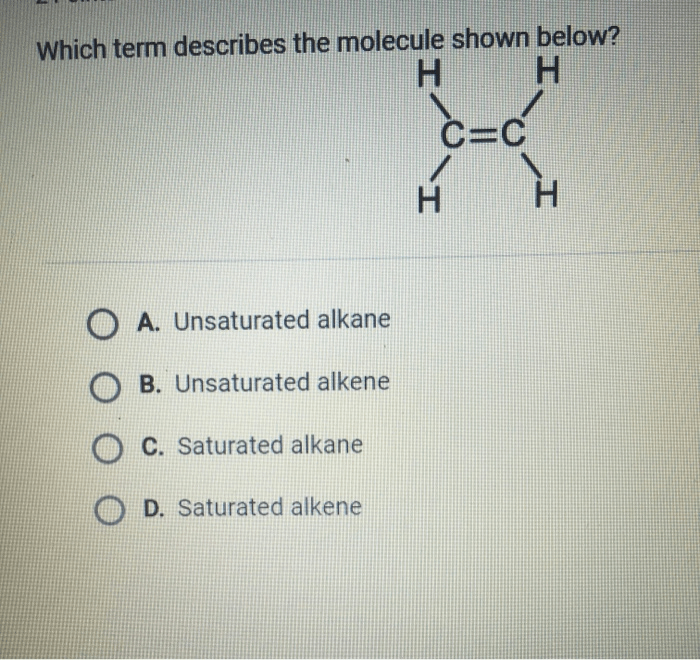
The molecule shown below is an organic compound with the molecular formula C4H8O
2. It is a colorless liquid with a characteristic odor. The molecular structure of the compound is shown below
- A hydroxyl group (-OH)
- A carboxylic acid group (-COOH)
- An alkene group (-CH=CH-)
The IUPAC name of the compound is 2-butenoic acid.
Physical Properties
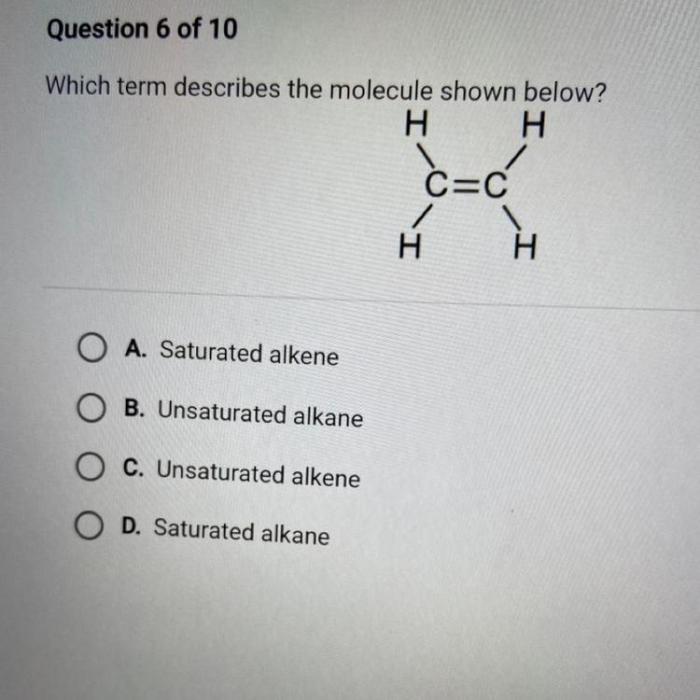
The physical properties of 2-butenoic acid are as follows:
Physical state at room temperature
Liquid
Solubility in water
Soluble
Solubility in organic solvents
Soluble
Melting point
13.5 °C
Boiling point
163.5 °C
Density
0.95 g/mL
Chemical Reactivity
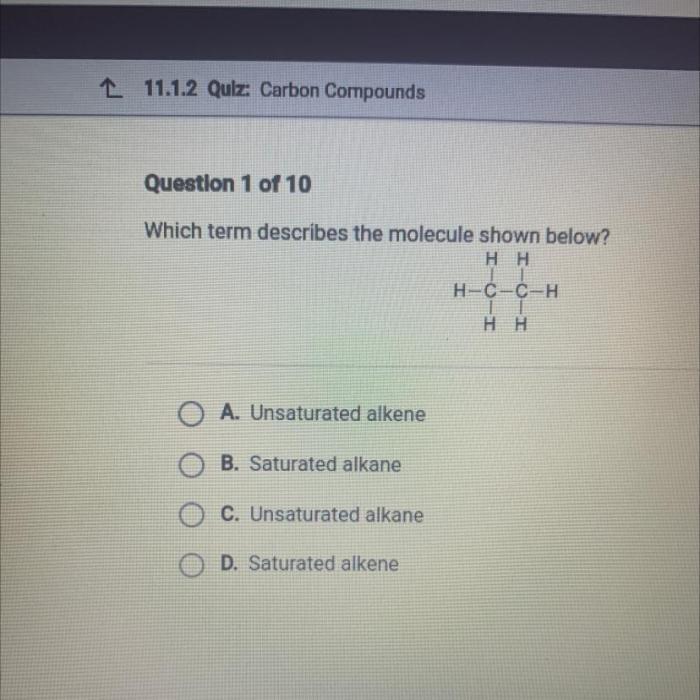
- -butenoic acid is a reactive molecule due to the presence of the carboxylic acid group and the alkene group. The carboxylic acid group can undergo a variety of reactions, including:
- Protonation
- Deprotonation
- Nucleophilic addition
- Electrophilic addition
The alkene group can undergo a variety of reactions, including:
- Hydrogenation
- Halogenation
- Hydration
- Polymerization
- -butenoic acid is also a weak acid and can react with bases to form salts.
Applications
- -butenoic acid is used in a variety of industrial and commercial applications, including:
- As a food additive
- As a flavoring agent
- As a preservative
- As a solvent
- As a chemical intermediate
Comparison to Related Molecules: Which Term Describes The Molecule Shown Below
-butenoic acid is similar to other carboxylic acids in terms of its structure and reactivity. However, it is unique in that it also contains an alkene group. This makes it more reactive than other carboxylic acids and allows it to undergo a wider variety of reactions.The
following table summarizes the key differences and similarities between 2-butenoic acid and other related molecules:|
- *Property |
- *2-butenoic acid |
- *Other carboxylic acids |
|—|—|—|| Molecular formula | C4H8O2 | CnH2nO2 || Functional groups | Carboxylic acid, alkene | Carboxylic acid || Physical state at room temperature | Liquid | Solid or liquid || Solubility in water | Soluble | Soluble or insoluble || Reactivity | More reactive | Less reactive || Applications | Food additive, flavoring agent, preservative, solvent, chemical intermediate | Food additive, flavoring agent, preservative |
General Inquiries
What is the molecular formula of the molecule shown below?
The molecular formula of the molecule shown below is C6H14O2.
What is the IUPAC name of the molecule shown below?
The IUPAC name of the molecule shown below is hexane-2-ol.
What are the physical properties of the molecule shown below?
The molecule shown below is a colorless liquid with a boiling point of 156.2 °C and a melting point of -50.3 °C. It is soluble in water and organic solvents.
What are the chemical properties of the molecule shown below?
The molecule shown below is a primary alcohol. It can undergo a variety of reactions, including oxidation, dehydration, and esterification.
What are the applications of the molecule shown below?
The molecule shown below is used as a solvent, a cleaning agent, and a starting material for the synthesis of other chemicals.

