Moving Nervously Because of Embarrassment delves into the intricate relationship between embarrassment and its physical, social, cognitive, and physiological manifestations. This exploration unravels the complex interplay between our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors when faced with situations that trigger feelings of self-consciousness.
Embarrassment can manifest in a myriad of ways, from subtle body language cues to more pronounced physiological responses. Understanding the mechanisms underlying these reactions is crucial for navigating social interactions with confidence and grace.
Nervous Body Language: Moving Nervously Because Of Embarrassment

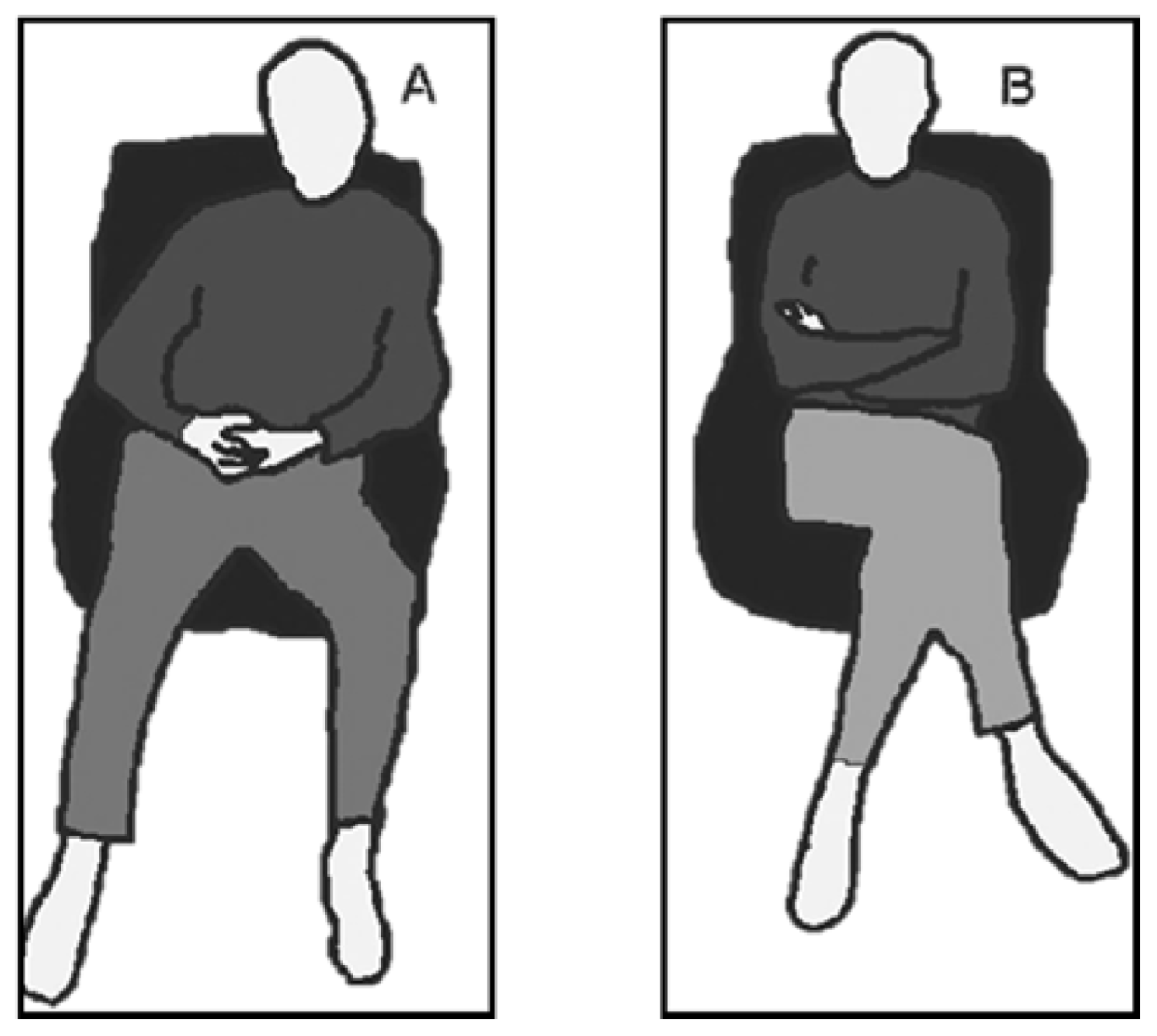
Nervousness due to embarrassment manifests in various physical reactions, known as nervous body language. These include fidgeting, blushing, and avoiding eye contact. Fidgeting, such as hand wringing or foot tapping, serves as a means of releasing pent-up energy and tension.
Blushing, a physiological response, occurs when blood vessels in the face dilate, causing a red tint. Avoiding eye contact, a common indicator of discomfort or anxiety, can be a subconscious attempt to avoid judgment or confrontation.
Specific Body Language Cues
- Fidgeting (e.g., hand wringing, foot tapping)
- Blushing
- Avoiding eye contact
- Clenched fists
- Tense posture
These physical reactions stem from the body’s natural response to perceived threats or uncomfortable situations. The sympathetic nervous system activates, triggering a “fight-or-flight” response that prepares the body for action. This physiological arousal manifests as the observed nervous body language.
Social Implications of Nervousness
Nervous behavior can significantly impact social interactions. Embarrassment can hinder communication by making individuals less likely to speak up or share their opinions. Relationships may also be affected, as nervousness can lead to misinterpretations and strained interactions. Individuals may withdraw from social situations to avoid feeling embarrassed, which can further isolate them.
Strategies for Coping with Nervousness
- Practice relaxation techniques (e.g., deep breathing, meditation)
- Challenge negative self-talk
- Focus on positive self-affirmations
- Seek support from trusted individuals
- Engage in gradual exposure to anxiety-provoking situations
By employing these strategies, individuals can gradually reduce their nervousness and improve their social interactions.
Cognitive Factors Contributing to Nervousness

Embarrassment-induced nervousness is influenced by cognitive processes. Negative self-talk, or the tendency to dwell on negative thoughts about oneself, can exacerbate nervousness. Self-consciousness, or the preoccupation with how one is perceived by others, can also contribute to feelings of anxiety and embarrassment.
Cognitive Restructuring Techniques
- Identifying and challenging negative thoughts
- Replacing negative thoughts with positive ones
- Focusing on realistic and achievable goals
- Developing a more positive self-image
Cognitive restructuring techniques aim to alter the negative thought patterns that contribute to nervousness. By reframing their thoughts and focusing on their strengths, individuals can reduce their feelings of anxiety and embarrassment.
Physiological Responses to Embarrassment

Embarrassment triggers physiological responses in the body. The sympathetic nervous system releases hormones such as adrenaline, which increases heart rate and breathing. This physiological arousal prepares the body for a fight-or-flight response.
Physical Symptoms of Embarrassment, Moving nervously because of embarrassment
- Increased heart rate
- Rapid breathing
- Sweating
- Flushing
- Shaking
These physical symptoms are the body’s natural response to the perceived threat of embarrassment. The intensity of the response can vary depending on the individual and the situation.
Cultural Influences on Nervousness
Cultural norms and expectations shape the experience of nervousness due to embarrassment. In some cultures, embarrassment is considered a sign of weakness or shame, while in others it is viewed as a normal and even positive emotion. These cultural differences can influence the way individuals cope with and express embarrassment.
Cultural Factors Influencing Nervousness
- Cultural expectations about appropriate behavior
- Socialization practices that emphasize the importance of avoiding embarrassment
- Cultural values that prioritize collectivism or individualism
By understanding the cultural context of embarrassment, individuals can better navigate social interactions and develop effective strategies for managing their nervousness.
FAQ Overview
What are some common body language cues that indicate embarrassment?
Fidgeting, blushing, avoiding eye contact, covering the face, and excessive sweating are all common body language cues that may indicate embarrassment.
How can embarrassment impact social interactions?
Embarrassment can hinder communication, damage relationships, and create a sense of isolation. It can also lead to avoidance behaviors and social anxiety.
What are some strategies for managing nervousness in social situations?
Cognitive restructuring techniques, such as challenging negative self-talk and focusing on positive aspects of oneself, can help manage nervousness. Additionally, practicing relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing and meditation, can help reduce anxiety levels.