Abdominal assessment hesi case study – Embark on an immersive journey into the realm of abdominal assessment with this comprehensive HESI case study. Delve into the intricacies of patient history, physical examination techniques, and imaging modalities, equipping yourself with the knowledge and skills to excel in this critical aspect of healthcare.
Through a systematic exploration of abdominal quadrants, auscultation, palpation, and percussion, you will gain a profound understanding of the methods used to evaluate abdominal structures and identify potential abnormalities. This in-depth analysis will empower you to make informed decisions and provide optimal patient care.
Patient History

A thorough patient history is essential for guiding the abdominal assessment. It provides insights into the patient’s current symptoms, past medical conditions, surgeries, and medications that may influence the examination findings.
Specifically, the history should focus on the following:
- Presenting symptoms:Abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, or other gastrointestinal complaints.
- Past medical history:Conditions such as peptic ulcer disease, inflammatory bowel disease, or abdominal surgeries.
- Surgical history:Previous abdominal surgeries can alter the anatomy and affect the examination findings.
- Medications:Certain medications, such as opioids or laxatives, can impact bowel function and abdominal examination results.
Understanding the patient’s history helps the healthcare provider interpret the physical examination findings more accurately and develop a differential diagnosis.
Physical Examination
A comprehensive abdominal examination involves a combination of inspection, palpation, percussion, and auscultation techniques.
- Inspection:Observing the abdomen for any visible abnormalities, such as distension, scars, or hernias.
- Palpation:Using the hands to feel the abdomen for tenderness, masses, or organ enlargement.
- Percussion:Tapping the abdomen to assess for fluid or gas accumulation.
- Auscultation:Listening to the abdomen with a stethoscope to evaluate bowel sounds and vascular bruits.
Each of these techniques provides valuable information about the underlying abdominal structures and helps in identifying potential abnormalities.
Abdominal Quadrants
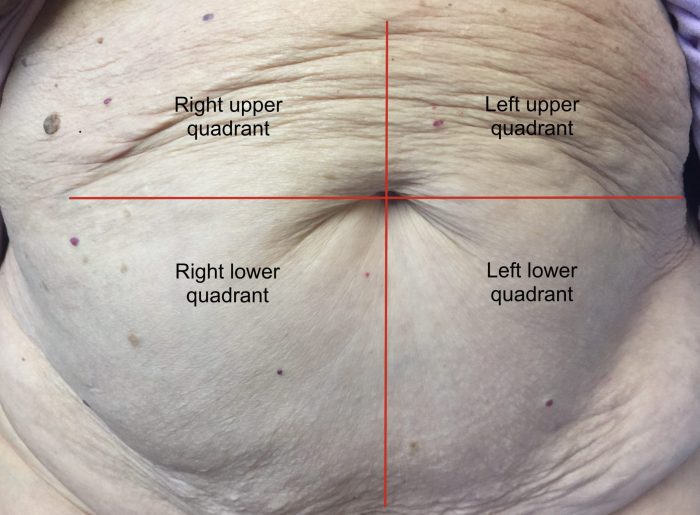
| Quadrant | Organs |
|---|---|
| Right Upper Quadrant | Liver, gallbladder, right kidney, right adrenal gland, part of the pancreas, duodenum |
| Left Upper Quadrant | Spleen, left kidney, left adrenal gland, part of the pancreas, stomach |
| Right Lower Quadrant | Cecum, appendix, right ovary (female), right ureter |
| Left Lower Quadrant | Sigmoid colon, left ovary (female), left ureter |
Understanding the abdominal quadrants helps in localizing pain or tenderness during the physical examination.
Abdominal Auscultation: Abdominal Assessment Hesi Case Study

Auscultation of the abdomen is crucial for assessing bowel sounds. Normal bowel sounds are characterized by high-pitched, gurgling noises that occur every 5-10 seconds.
Abnormalities in bowel sounds can indicate various conditions:
- Increased bowel sounds:Hyperactive peristalsis, as seen in diarrhea or early bowel obstruction.
- Decreased bowel sounds:Hypoactive or absent peristalsis, as seen in paralytic ileus or late bowel obstruction.
- Absent bowel sounds:Complete absence of peristalsis, often associated with peritonitis or advanced bowel obstruction.
Auscultation helps in identifying these abnormalities and guiding further diagnostic investigations.
Abdominal Palpation
Abdominal palpation is performed using light, deep, and ballottement techniques.
- Light palpation:Gentle pressure applied to assess superficial structures, such as the abdominal wall and tenderness.
- Deep palpation:Deeper pressure applied to assess deeper structures, such as the liver, spleen, and kidneys.
- Ballottement:A technique used to detect fluid-filled organs, such as the bladder or uterus.
Palpation provides information about the size, shape, consistency, and tenderness of abdominal organs.
Questions and Answers
What is the significance of abdominal auscultation?
Abdominal auscultation is essential for assessing bowel sounds, which can provide valuable information about gastrointestinal function. Normal bowel sounds indicate regular peristalsis, while abnormal sounds, such as hyperactive or hypoactive bowel sounds, may suggest underlying digestive issues.
How does abdominal palpation aid in organ evaluation?
Abdominal palpation allows clinicians to assess the size, shape, and consistency of abdominal organs. By applying light, deep, and ballottement techniques, healthcare professionals can detect masses, tenderness, or other abnormalities that may indicate underlying pathology.
What role does abdominal imaging play in abdominal assessment?
Abdominal imaging techniques, such as X-rays, ultrasound, and CT scans, provide detailed anatomical images of abdominal structures. These imaging modalities can confirm or rule out suspected abnormalities, such as organ enlargement, fluid accumulation, or masses, aiding in the diagnostic process.