Label the components of a glass ph combination electrode – Labeling the components of a glass pH combination electrode is crucial for understanding its operation and applications. This electrode plays a vital role in pH measurement, and its components work together to generate an electrical potential that corresponds to the pH of a solution.
This article delves into the intricacies of a glass pH combination electrode, providing a detailed diagram and explaining the purpose and function of each component. We will explore the principle of operation, discuss its applications, and highlight the importance of maintenance and calibration.
Label the Components of a Glass pH Combination Electrode
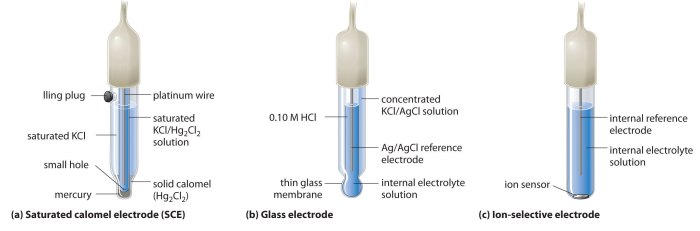
A glass pH combination electrode is a device used to measure the pH of a solution. It consists of a glass bulb, a reference electrode, a salt bridge, and a pH-sensitive membrane.
The glass bulb is a thin-walled glass sphere that contains the pH-sensitive membrane. The reference electrode is a metal electrode that is immersed in a solution of known pH. The salt bridge is a porous material that connects the reference electrode to the solution being tested.
The pH-sensitive membrane is a thin layer of glass that is coated with a pH-sensitive material. When the membrane is exposed to a solution, the pH of the solution causes the membrane to generate an electrical potential. The magnitude of the electrical potential is proportional to the pH of the solution.
Diagram of a Glass pH Combination Electrode
[Gambar diagram elektroda kombinasi pH kaca di sini]
- Glass bulb
- Reference electrode
- Salt bridge
- pH-sensitive membrane
Operation of a Glass pH Combination Electrode: Label The Components Of A Glass Ph Combination Electrode
The principle of operation of a glass pH combination electrode is based on the Nernst equation, which states that the electrical potential of a cell is proportional to the difference in concentration of the ions being measured.
In the case of a glass pH combination electrode, the ions being measured are hydrogen ions. When the membrane is exposed to a solution, the hydrogen ions in the solution diffuse through the membrane and react with the pH-sensitive material.
This reaction causes the membrane to generate an electrical potential.
The magnitude of the electrical potential is proportional to the pH of the solution. The more acidic the solution, the higher the concentration of hydrogen ions and the greater the electrical potential.
Role of the Reference Electrode and Salt Bridge
The reference electrode provides a stable electrical potential against which the electrical potential of the pH-sensitive membrane can be measured. The salt bridge connects the reference electrode to the solution being tested and allows the ions in the solution to flow between the reference electrode and the membrane.
Applications of a Glass pH Combination Electrode
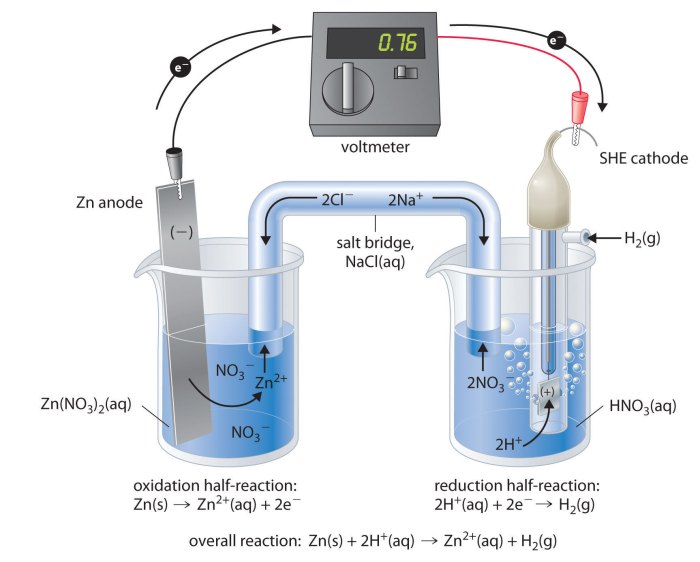
Glass pH combination electrodes are used in a wide variety of applications, including:
- Water quality monitoring
- Food and beverage production
- Pharmaceutical manufacturing
- Environmental monitoring
- Medical diagnostics
Glass pH combination electrodes are relatively inexpensive and easy to use, making them a popular choice for pH measurement.
Advantages and Limitations of Using Glass pH Combination Electrodes
Glass pH combination electrodes offer several advantages, including:
- Accuracy
- Reliability
- Ease of use
- Low cost
However, glass pH combination electrodes also have some limitations, including:
- Fragility
- Sensitivity to temperature
- Limited pH range
Comparison of Glass pH Combination Electrodes with Other pH Measurement Techniques
Glass pH combination electrodes are the most widely used pH measurement technique. However, there are a number of other pH measurement techniques available, including:
- Colorimetric pH indicators
- pH paper
- Ion-selective electrodes
- Solid-state pH electrodes
Each of these techniques has its own advantages and limitations. Glass pH combination electrodes are generally the most accurate and reliable, but they are also the most expensive.
Maintenance and Calibration of a Glass pH Combination Electrode
To ensure the accuracy and longevity of a glass pH combination electrode, it is important to follow proper maintenance and calibration procedures.
Proper Maintenance Procedures
The following are some tips for proper maintenance of a glass pH combination electrode:
- Store the electrode in a cool, dry place when not in use.
- Rinse the electrode with distilled water before and after each use.
- Do not touch the pH-sensitive membrane with your fingers.
- Do not immerse the electrode in organic solvents or strong acids or bases.
Importance of Calibration, Label the components of a glass ph combination electrode
It is important to calibrate a glass pH combination electrode regularly to ensure its accuracy. The frequency of calibration will depend on the frequency of use and the accuracy requirements of the application.
To calibrate a glass pH combination electrode, you will need a pH buffer solution of known pH. Immerse the electrode in the buffer solution and adjust the calibration knob until the meter reads the correct pH.
Factors that Can Affect the Accuracy and Lifespan of a Glass pH Combination Electrode
The following factors can affect the accuracy and lifespan of a glass pH combination electrode:
- Temperature
- pH of the solution being tested
- Presence of interfering ions
- Age of the electrode
Popular Questions
What is the purpose of a glass pH combination electrode?
A glass pH combination electrode measures the pH of a solution by generating an electrical potential that corresponds to the hydrogen ion concentration.
How does the pH-sensitive membrane work?
The pH-sensitive membrane is made of a special glass that allows hydrogen ions to pass through. The difference in hydrogen ion concentration between the inside and outside of the membrane creates an electrical potential.
What is the role of the reference electrode?
The reference electrode provides a stable electrical potential that is used as a reference point for the measurement.