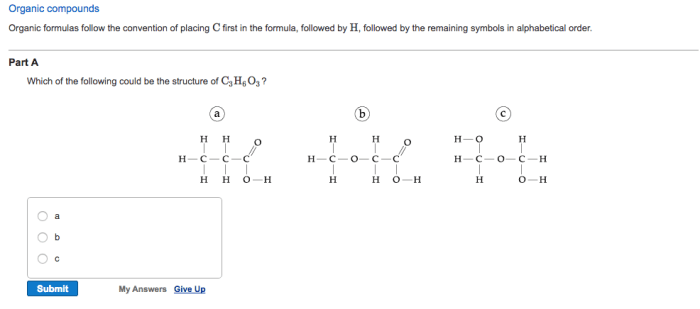
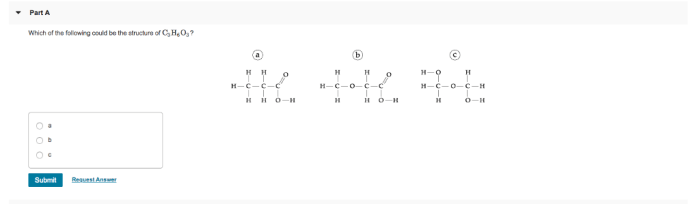
Which of the following could be the structure of C3H6O3? This question delves into the realm of organic chemistry, exploring the molecular makeup and properties of a compound with the formula C3H6O3. As we embark on this journey of discovery, we will unravel the intricacies of its chemical structure, identify its isomers, and delve into its physical and chemical characteristics.
Prepare to be captivated as we uncover the fascinating world of C3H6O3.
C3H6O3, with its unique molecular arrangement, presents a diverse range of isomers, each possessing distinct structural features. These isomers, like pieces of a puzzle, share the same molecular formula but differ in their atomic connectivity. Understanding these structural variations is crucial for comprehending the compound’s reactivity and properties.
Chemical Structure of C3H6O3: Which Of The Following Could Be The Structure Of C3h6o3
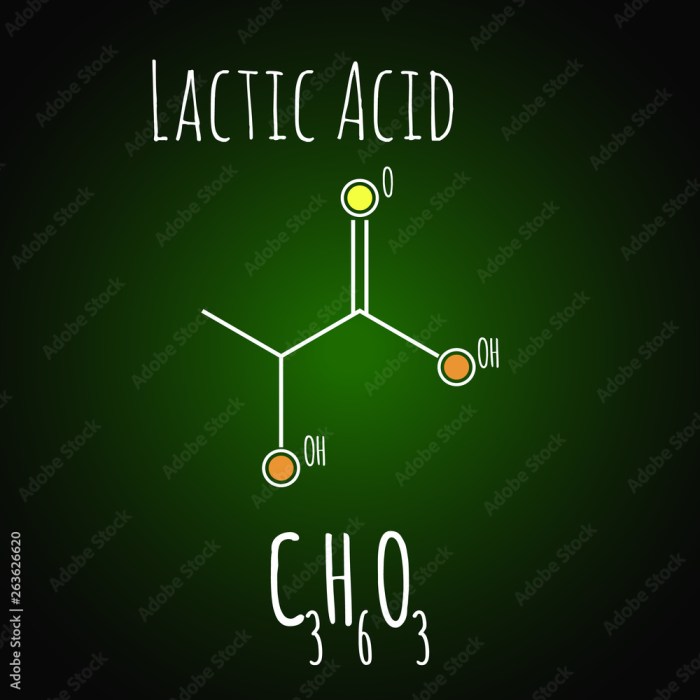
C3H6O3 is a molecular formula that represents a compound containing three carbon atoms, six hydrogen atoms, and three oxygen atoms. This molecular formula can correspond to several isomers, which are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements.
Isomers of C3H6O3
The three possible isomers of C3H6O3 are:
-
-*Propanal (propanone)
A ketone with the structure CH3CH2CHO.
-*Propanol (1-propanol)
A primary alcohol with the structure CH3CH2CH2OH.
-*Methyl acetate
An ester with the structure CH3COOCH3.
These isomers differ in their structural arrangement and functional groups. Propanal contains a ketone functional group (C=O), propanol contains a primary alcohol functional group (-OH), and methyl acetate contains an ester functional group (-COOCH3).
Functional Groups in C3H6O3
The functional groups present in the isomers of C3H6O3 are:
-
-*Ketone group (C=O)
Propanal contains a ketone group, which is characterized by a carbon-oxygen double bond. Ketones are reactive and can undergo various reactions, including nucleophilic addition and oxidation.
-*Primary alcohol group (-OH)
Propanol contains a primary alcohol group, which is characterized by a hydroxyl group (-OH) bonded to a carbon atom. Primary alcohols are reactive and can undergo reactions such as oxidation and esterification.
-*Ester group (-COOCH3)
Methyl acetate contains an ester group, which is characterized by a carbon-oxygen double bond and an oxygen atom bonded to an alkyl group. Esters are relatively unreactive and are often used as solvents or fragrances.
Physical and Chemical Properties of C3H6O3
The physical and chemical properties of the isomers of C3H6O3 vary depending on their structural arrangement and functional groups.| Property | Propanal | Propanol | Methyl Acetate ||—|—|—|—|| Molecular weight | 58.08 g/mol | 60.10 g/mol | 74.08 g/mol || Melting point |
- 81 °C |
- 126 °C |
- 98 °C |
| Boiling point | 56 °C | 97 °C | 57 °C || Density | 0.81 g/cm³ | 0.80 g/cm³ | 0.93 g/cm³ || Solubility in water | Slightly soluble | Soluble | Insoluble || Reactivity | Reactive | Moderately reactive | Relatively unreactive |
Synthesis of C3H6O3
The isomers of C3H6O3 can be synthesized using various methods.Propanal
- Oxidation of propanol using an oxidizing agent such as potassium permanganate or chromic acid.
- Hydroformylation of ethene using carbon monoxide and hydrogen in the presence of a catalyst.
Propanol
- Hydration of propene using water in the presence of an acid catalyst.
- Reduction of propanal using a reducing agent such as sodium borohydride or lithium aluminum hydride.
Methyl Acetate
- Esterification of methanol and acetic acid in the presence of an acid catalyst.
- Reaction of acetyl chloride with methanol.
Applications of C3H6O3, Which of the following could be the structure of c3h6o3
The isomers of C3H6O3 have various applications in different industries.Propanal
- As a solvent in the paint and coating industry.
- As a flavoring agent in the food industry.
- As a starting material for the synthesis of other chemicals.
Propanol
- As a solvent in the pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries.
- As a cleaning agent in the household and industrial sectors.
- As a fuel in some applications.
Methyl Acetate
- As a solvent in the paint and coating industry.
- As a flavoring agent in the food industry.
- As a starting material for the synthesis of other chemicals.
FAQ Corner
What is the molecular weight of C3H6O3?
The molecular weight of C3H6O3 is 74.08 g/mol.
What is the IUPAC name of C3H6O3?
The IUPAC name of C3H6O3 is 1-propanol-2-one.
What is the boiling point of C3H6O3?
The boiling point of C3H6O3 is 97.2 °C.